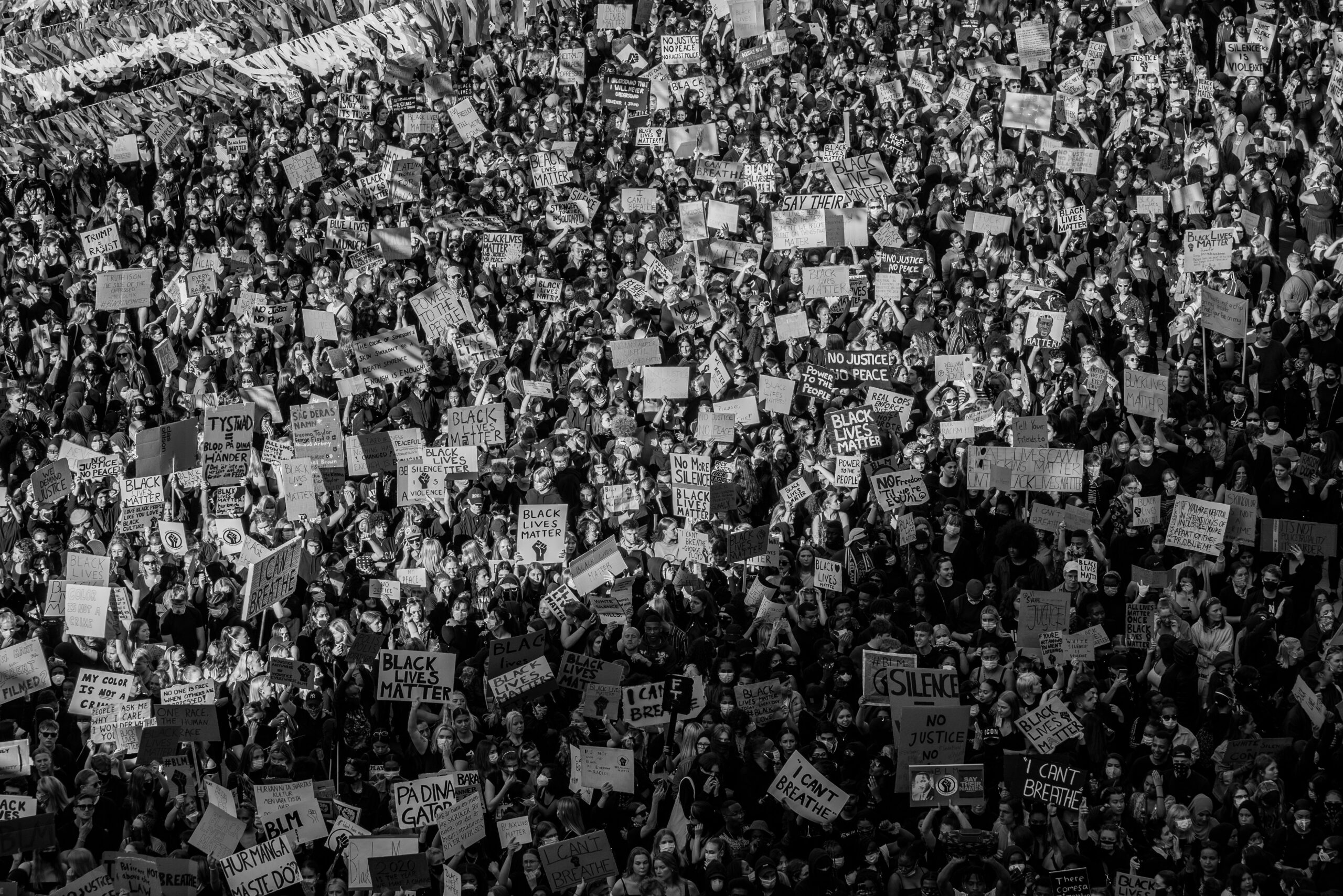A pro-Palestinian group has recently defaced a century-old portrait of Arthur James Balfour, the author of the Balfour Declaration, at the University of Cambridge in England. The group, Palestine Action, sprayed red paint and slashed the painting as a means of drawing attention to the ongoing conflicts in Palestine and the oppression faced by the Palestinian people. The destruction of the portrait serves as a symbolic act against Balfour’s support for the establishment of a Jewish homeland in Palestine, which ultimately led to the creation of Israel. This incident reflects a growing trend of defacing art as a form of protest, with environmentalists and pro-Palestinian activists targeting various artworks in recent years.
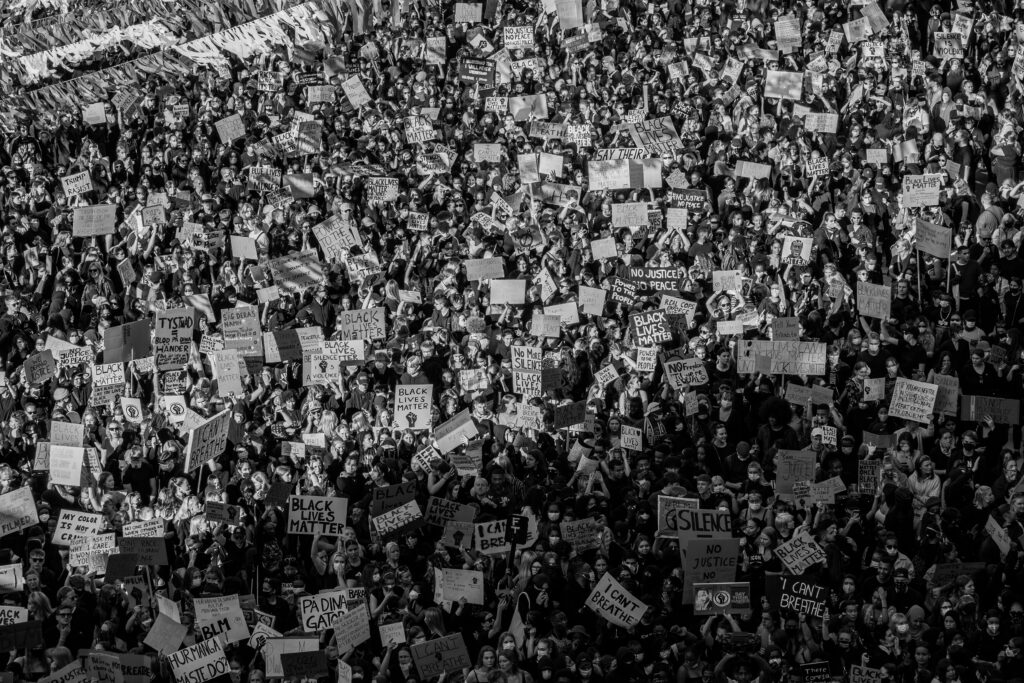
Background
Arthur James Balfour and the Balfour Declaration
Arthur James Balfour, a British official, played a significant role in the establishment of Israel through the Balfour Declaration. The Balfour Declaration, issued in 1917, expressed support for the establishment of a national home for the Jewish people in Palestine. Balfour’s declaration was instrumental in laying the groundwork for the creation of Israel three decades later.
The Establishment of Israel
The establishment of the State of Israel in 1948 fulfilled the aspirations of the Zionist movement, which sought a homeland for Jewish people. The United Nations played a crucial role in the partitioning of Palestine, leading to the creation of Israel. The long-standing conflict between Israelis and Palestinians over the land has been a central issue in the Middle East.
The Palestinian Perspective
The Palestinian perspective on the establishment of Israel differs significantly from the Israeli narrative. Palestinians, who have long inhabited the land that is now Israel, view the creation of Israel as a violation of their rights and as a result of colonialism. They argue that the Balfour Declaration and the subsequent actions of the British government led to the dispossession and displacement of Palestinians.
Defacing the Portrait
The Pro-Palestinian Group’s Actions
Palestine Action, a pro-Palestinian group, took responsibility for defacing the portrait of Arthur James Balfour at Trinity College, Cambridge. The group believes that Balfour’s support for the establishment of Israel resulted in the oppression and bloodshed of the Palestinian people. By defacing the portrait, they aimed to draw attention to the ongoing suffering of the Palestinians.
Video of the Incident
Palestine Action posted a video of the incident, which showed a protester spraying red paint on the portrait and subsequently slashing it with a sharp object. The video captured the act of defacement and the group’s intent to convey their message through this provocative action.
Group’s Statement on the Motive
According to Palestine Action, the motive behind defacing the portrait was to highlight the injustices suffered by the Palestinian people. They argue that Balfour’s actions, as outlined in the Balfour Declaration, contributed to the dispossession and suffering of Palestinians. The group considers the land of Palestine to be rightfully belonging to the Palestinians and believes that Balfour had no authority to give it away.
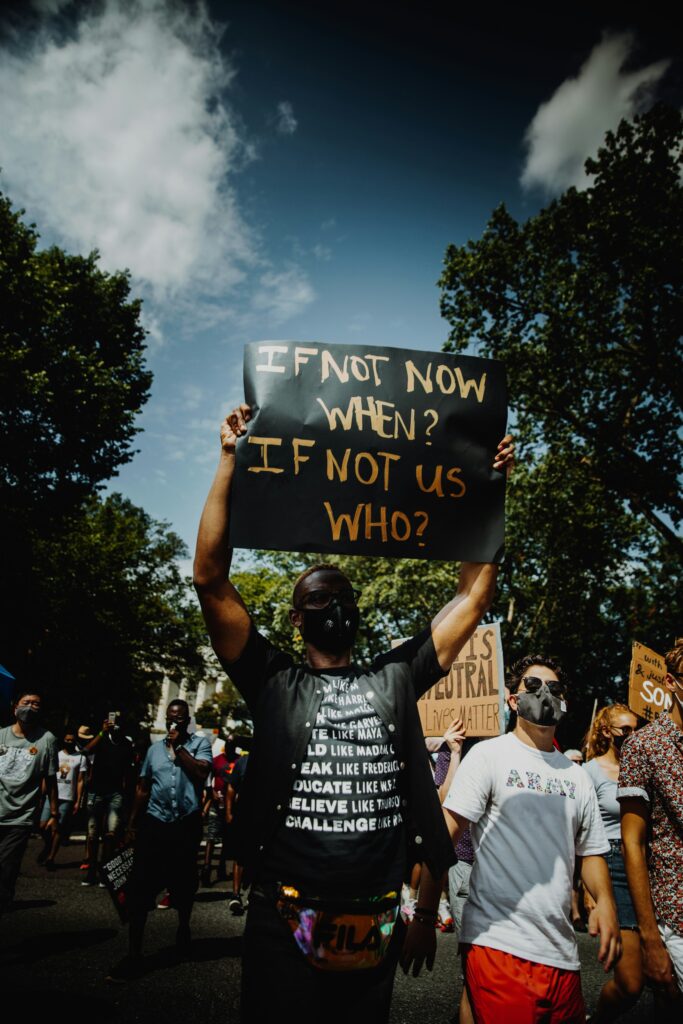
Reactions and Consequences
Trinity College’s Response
Trinity College expressed regret over the damage caused to the portrait during public opening hours. The college notified the police about the incident and condemned the act of defacement. Trinity College, being associated with Balfour and his portrait, was faced with the challenge of addressing the incident while considering the values of freedom of expression and the protection of art.
Police Investigation
Cambridge police initiated an investigation into the incident of criminal damage. They arrived at the scene to assess the extent of the damage and gather evidence. The investigation aimed to identify the individuals involved in the defacement and hold them accountable for their actions.
Public Opinion
Public opinion on the defacement of the portrait was divided. Some viewed the act as an act of vandalism and disrespect for art, while others saw it as a form of protest against perceived injustices. The incident sparked a conversation about the limits of protest and the role of art in shaping public discourse.
Defacing Art as a Protest Tactic
Environmentalists’ Use of Defacing Art
Defacing art as a protest tactic has gained popularity in recent years, particularly among environmentalists. They have targeted famous paintings by renowned artists such as van Gogh, Vermeer, and Monet to draw attention to environmental issues. These acts of defacement often involve covering or protecting the artworks, minimizing physical damage.
Other Instances of Defacing Art
The defacement of art is not limited to environmental protests. In recent years, art has been defaced to protest various issues, including political views, social injustices, and historical narratives. These acts aim to disrupt and challenge prevailing narratives through provocative and often controversial means.
Impact and Effectiveness
The impact and effectiveness of defacing art as a form of protest continue to be debated. While some argue that such acts generate attention and provoke discussions, others believe that they undermine the sanctity of art and divert attention from the message being conveyed. The effectiveness of these tactics in achieving long-term change remains a subject of exploration and analysis.

Pro-Palestinian Art Protests in Recent Weeks
Disrupting Israeli Artist’s Show in New York
In a recent incident, a few dozen protesters disrupted the opening of an Israeli artist’s show at a Manhattan gallery. The protesters sought to bring attention to the Israeli-Palestinian conflict and express solidarity with the Palestinian cause. The incident highlighted the growing trend of pro-Palestinian art activism in various parts of the world.
Protesting at Jewish and Modern Art Museums
Pro-Palestinian activists have targeted Jewish and modern art museums to express their grievances. These demonstrations often involve chanting slogans, interrupting events, and demanding the liberation of Palestine. These actions aim to challenge narratives presented within the art world and draw attention to the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
Growing Movement of Pro-Palestinian Art Activism
The movement of pro-Palestinian art activism has gained momentum in recent years, with artists, activists, and individuals using various art forms to express their solidarity with the Palestinian people. From visual art to performance art, these expressions serve as a means of communication, creating awareness, and challenging dominant narratives surrounding the conflict.
Defacing Art and Freedom of Expression
Debate on the Limits of Protesting
The defacement of art raises questions about the limits of protesting and freedom of expression. While freedom of expression is valued in democratic societies, there are ongoing debates about the appropriateness and legality of certain forms of protest, including the defacement of art. Determining the boundaries of protest and expression remains a complex challenge.
Balancing Artistic Freedom and Activism
Artistic freedom and activism often intersect, but the question of how to strike a balance between the two is a matter of ongoing discussion. Artists and activists engage in a delicate balance, as artistic expression can be a powerful tool for activism, while activism can impact the integrity and preservation of art.
Legal Consequences of Art Defacement
Art defacement carries potential legal consequences. Depending on the jurisdiction, those responsible for defacing art can face charges ranging from vandalism to destruction of cultural heritage. The legal response to such acts varies, and courts must navigate the complexities of balancing freedom of expression with the protection of cultural artifacts.
The Israeli-Hamas Conflict and its Impact on Activism
Recent Conflict in Gaza
The Israeli-Hamas conflict in recent years has seen periods of heightened violence and tensions. These conflicts have led to loss of life, displacement, and widespread destruction. The human toll of these conflicts has spurred activism and protests worldwide, with various groups expressing support for either the Israeli or Palestinian cause.
Heightened Pro-Palestinian Activism
The Israeli-Hamas conflict has resulted in a surge of pro-Palestinian activism globally. Activists, artists, and individuals who oppose Israeli policies have organized demonstrations, engaged in boycotts, and used different forms of art to draw attention to the plight of the Palestinian people. The conflict has further polarized public opinion regarding the Israeli-Palestinian conflict.
Connection Between Art Defacement and the Conflict
The defacement of Balfour’s portrait at Trinity College is directly linked to the Israeli-Hamas conflict. Palestine Action, the group responsible for the defacement, sought to bring attention to the ongoing bloodshed and oppression experienced by Palestinians. The incident reflects the way in which the conflict influences activism and shapes the strategies adopted by protesters.
Discussion on the Role of Universities in Controversial Art
Trinity College’s Association with Balfour
Trinity College’s association with Arthur James Balfour raises questions regarding its responsibility in displaying controversial figures’ portraits. Balfour’s role in the establishment of Israel and the repercussions faced by Palestinians make his portrait a subject of controversy. Universities must navigate the tension between displaying historical figures and acknowledging the concerns of marginalized communities.
Responsibility of Universities in Protecting Art
Universities bear the responsibility of protecting art and preserving historical artifacts within their institutions. This duty extends to ensuring the security and safety of artworks, maintaining an environment that fosters freedom of expression, and addressing controversies surrounding displayed art. Universities must balance competing interests to ensure the preservation and protection of both art and diverse perspectives.
Ethics of Displaying Controversial Figures’ Portraits
The display of controversial figures’ portraits raises ethical questions. Institutions must critically examine the implications of displaying individuals associated with controversial policies and actions. Engaging in dialogue and seeking input from diverse stakeholders can help institutions navigate the ethical challenges associated with displaying portraits that represent contested histories.
Art Restoration and Preservation
Restoration Efforts for Defaced Artworks
Art restoration professionals are often called upon to repair and restore defaced artworks. The restoration process involves assessing the damage, developing a conservation plan, and employing techniques to repair and preserve the artwork. Restoration efforts aim to return the artwork to its original condition while considering historical significance and artistry.
Challenges Faced in Preserving Historical Art
Preserving historical art poses unique challenges due to factors such as age, fragility, and the presence of damage or decay. Beyond physical deterioration, artworks may also present complex narratives and historical context that require careful preservation. Experts in art conservation and preservation work to overcome these challenges to ensure the longevity and accessibility of historical art.
Balancing Conservation with Historical Significance
Conserving art involves striking a delicate balance between preservation and the historical significance of the artwork. Preservation techniques must be carefully implemented to ensure the artwork’s longevity while preserving its authenticity and intended meaning. This balance is particularly important when dealing with controversial or defaced artworks with heightened historical significance.
Conclusion
Continued Conversation on Art Activism
The defacement of Arthur James Balfour’s portrait at Trinity College has sparked a conversation on the effectiveness and ethics of art activism. The incident highlights the intersection of art, activism, and historical narratives in protests surrounding the Israeli-Palestinian conflict. This ongoing conversation seeks to explore the impact of art as a form of protest and its role in shaping public discourse.
Implications for Future Protests
The defacement of Balfour’s portrait and the subsequent reactions have implications for future protests. Pro-Palestinian activists and other groups may continue to employ art as a means of protest, challenging prevailing narratives and advocating for change. The incident at Trinity College underscores the need for institutions and society at large to engage in constructive dialogue about the role of art in expressing dissent and seeking justice.
Long-Term Effects on the Art World
The defacement of art and the rise of art activism have the potential to have long-term effects on the art world. Institutions may reassess their display policies and engage in discussions about the representation of controversial figures. Artists and activists may continue to use art as a powerful tool for social change, challenging traditional norms and fostering dialogue on critical social and political issues. The intersection of art and activism will likely shape the future of the art world and its relationship with broader societal debates.